The well-known ransomware TeslaCrypt has gone through continuous evolution of cyber racketeering mechanisms. Last February, it targeted mostly gamers, and later on the ransomware turned into a more flexible extortion tool with wide attack surface and advanced encryption routine.
The first two versions of TeslaCrypt weren’t foolproof because the perpetrators implemented Advanced Encryption Standard in a very inefficient way. Besides, the decryption keys were stored inside an easily accessible file on a contaminated computer rather than be transmitted to a remote Command and Control server.
These flaws let security experts deliver a data recovery technique through the use of a specially crafted tool named TeslaDecoder. Thanks to the researchers, the victims of TeslaCrypt had the chance to retrieve their encrypted files for months at once. However, this period ended abruptly as soon as TeslaCrypt 3.0 came out.
The new version of the ransomware has updated features and a number of tweaks which makes the decrypter inefficient. Apparently, the creators of TeslaCrypt have realized their previous mistakes and corrected the flaws.
Currently, TeslaCrypt 3.0 does not keep AES keys on the targeted machine anymore. This fundamental modification of the key exchange algorithm, alongside the impracticability of brute-forcing the crypto proper, renders the Trojan uncrackable for long time.
Now it is easier to determine the version and find out whether it’s possible to get around the encryption due to the fact that TeslaCrypt uses specific markers as new editions are released. These markers include file extensions and the names of ransom note documents.
The latest version of TeslaCrypt appends every encrypted file with .mp3 extension. For example, a filename ‘random.jpg’ becomes ‘random.jpg.mp3’ as a result of the attack. If users face this sample, they are bound to redeem their personal information by paying the hackers.
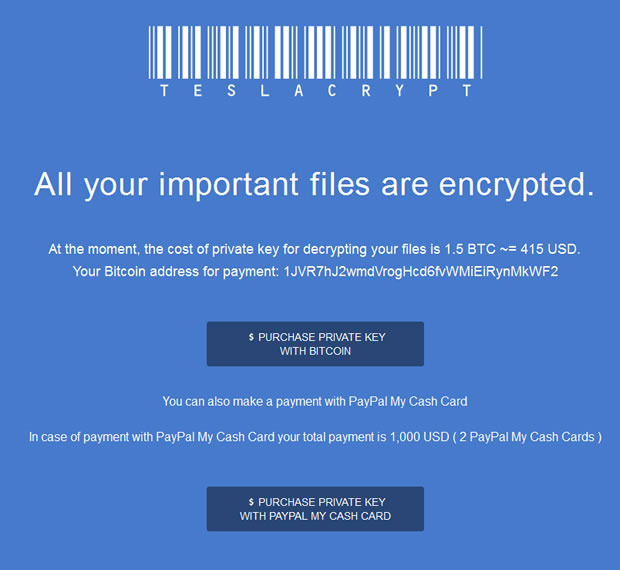
TeslaCrypt 3.0 provides the entirety of recovery and payment directions in .htm, .txt and .png files titled _H_e_l_p_RECOVER_INSTRUCTIONS+(3 characters). These documents can be found inside each folder holding encrypted data. The ransom notes state that the victim must submit a Bitcoin equivalent of 500 USD to get the proprietary files back. Also, the amount doubles if the victim doesn’t pay up within a 72-hour deadline.
TeslaCrypt 3.0 uses a Domain Generation Algorithm to create several relevant payment pages for every contaminated person. The extortionists also indicate a unique Tor gateway address as an alternative online spot for financial transactions. For that reason, the whole campaign is skillfully protected against tracking and attribution, which explains why the criminals are still on the loose.
Regarding the propagation, TeslaCrypt creators didn’t reinvent the wheel. They have been leveraging an efficient mix of social engineering and exploit kits to deliver the ransomware payload. A blatant example of this activity is the hack of The Independent new site, which hit the global security headlines last November. By compromising the blog section of the website, the hackers were able to run an exploit that stealthily downloaded TeslaCrypt to the visitors’ computers. The Angler exploit kit used in this onslaught took advantage of vulnerabilities in outdated versions of Adobe Flash Player.
Phishing poses a standalone vector of serving this ransomware. The cyber criminals send out catchy emails which contain attachments disguised as invoices, payrolls, CVs or UPS tracking information. As soon as users opens the file, they unknowingly execute the infection on their computers.
TeslaCrypt prevention techniques stem is strongly recommended to update potentially vulnerable software like Adobe Flash and Java as soon as patches are available. In addition, PC users should stay away from suspicious emails and refrain from opening files attached to them. Yet, the most important thing for users is to back up their files regularly in order to protect them from ransomware attacks.